Metasurface For Microstrip-fed Slot Antennas
- Metasurface For Microstrip-fed Slot Antennas Long Range
- Metasurface For Microstrip-fed Slot Antennas Antenna
- Mu-near-zero Metasurface For Microstrip-fed Slot Antenna
- Metasurface For Microstrip-fed Slot Antennas For Sale
- Metasurface For Microstrip-fed Slot Antennas Ham Radio
Abstract
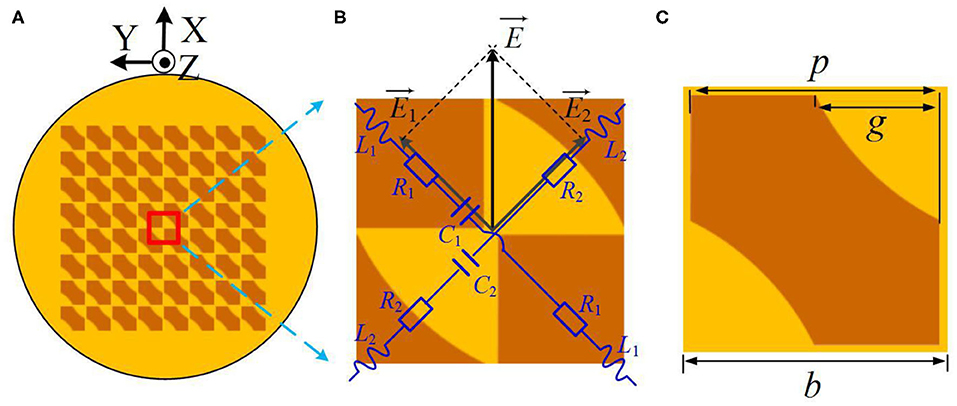
The metasurface concept has emerged as an advantageous reconfigurable antenna architecture for beam forming and wave-front shaping, with applications that include satellite and terrestrial communications, radar, imaging, and wireless power transfer. The metasurface antenna consists of an array of metamaterial elements distributed over an electrically large structure, each subwavelength in dimension and with subwavelength separation between elements. In the antenna configuration we consider, the metasurface is excited by the fields from an attached waveguide. Each metamaterial element can be modeled as a polarizable dipole that couples the waveguide mode to radiation modes. Distinct from the phased array and electronically-scanned-antenna architectures, a dynamic metasurface antenna does not require active phase shifters and amplifiers but rather achieves reconfigurability by shifting the resonance frequency of each individual metamaterial element. We derive the basic properties of a one-dimensional waveguide-fed metasurface antenna in the approximation in which the metamaterial elements do not perturb the waveguide mode and are noninteracting. We derive analytical approximations for the array factors of the one-dimensional antenna, including the effective polarizabilities needed for amplitude-only, phase-only, and binary constraints. Using full-wave numerical simulations, we confirm the analysis, modeling waveguides with slots or complementary metamaterial elements patterned into one of the surfaces.
Metasurface For Microstrip-fed Slot Antennas Long Range

 7 More
7 MoreMetasurface For Microstrip-fed Slot Antennas Antenna
- Received 27 June 2017
Mu-near-zero Metasurface For Microstrip-fed Slot Antenna
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevApplied.8.054048
© 2017 American Physical Society
Metasurface For Microstrip-fed Slot Antennas For Sale
Physics Subject Headings (PhySH)
- Abstract—A frequency-reconfigurable antenna designed using metasurface (MS) to operate at around 5 GHz is studied and proposed. The frequency-reconfigurable metasurfaced (FRMS) antenna is composed of a simple circular patch antenna and a circular MS with the same diameter of 40 mm and implemented using planar technology.
- By loading the metasurface on the microstrip slot antenna, linearly polarized (LP) waves from the source antenna are converted into circularly polarized (CP) waves. Then, by etching three more parasitic square cross gaps in the middle of the metasurface, enhanced impedance bandwidth and axial ratio bandwidth (ARBW) are achieved.
Metasurface For Microstrip-fed Slot Antennas Ham Radio
A meander stripline feed multiband microstrip antenna loaded with metasurface reflector (MSR) structure has been designed, analyzed and constructed that offers the wireless communication services for UHF/microwave RFID and WLAN/WiMAX applications. The proposed MSR assimilated antenna comprises planar straight forward design of circular shaped radiator with horizontal slots on it and 2D. A new design for a microstrip-fed slot antenna (MFSA) is proposed and developed for improving bandwidth, gain and reducing back radiation. In contrast with most unidirectional MFSA, a metasurface as a superstrate is employed to reduce the back-lobe radiation and enhance the gain without a metal reflector.